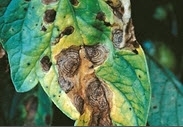
General Information
Groundnut is the third most important oilseed of the world as well as second greatest in India. It is also known as earthnuts, goober peas, monkey nuts, pygmy nuts and pea nuts in local language. It belongs to legume family. Depending upon variety and agronomic condition oil content of seed vary from 44-50%. Its oil is used in cooking, cosmetic, and soap making etc.
In India, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Himachal Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu are major groundnut growing states. Jhanshi, Hardoi, Sitapuri, Khiri, Unnav, Bareli, Eta, Muradabad, and Saharanpur are major groundnut growing areas of groundnut.