Climate
-
Temperature
20-30°C -
Rainfall
75-150cm -
Sowing Temperature
20-25°C -
Harvesting Temperature
20-30°C

















Well drained, deep, loamy soil with ground water table below 1.5-2m from the soil surface with adequate water holding capacity is ideal for sugarcane cultivation. It can tolerate considerable degree of acidity and alkalinity so it can be grown on soil, ranging from 5 to 8.5. If soil is low in pH (less than 5) add lime in soil and for high pH (more than 9.5) do gypsum application.
CO 419: High yielding but late maturing variety. Gives average yield of 500qtl/acre.
COS 767: Medium duration variety. Produces gur/Jaggery of good quality. Gives good yield when grown in heavy soils. Gives average yield of 330-420qtl/acre.
CO 1007: Medium duration variety. It is non-lodging and resistant to several pests. Suitable for heavy soil areas. Gives average yield of 330-420qtl/acre.
CO 66-17: It is late duration variety. It is resistant to lodging and drought conditions. Produces gur/Jaggery of good quality. Gives good results when grown in red rot disease free areas.
CO 1148: Medium duration variety. Applicable for late sowing. Good germinator with profuse tillering, excellent ratooning capacity. It produces medium quality gur. It is highly susceptible to red rot. It gives average yield of 375qtl/acre.
CO Pant 84211: It is an early maturing variety. The variety is released in 1991. The variety has good germination rate, tillering and ratooning ability. The average length of sugarcane is 2-2.5m and the weight is 800gm/sugarcane. Gives average yield of 290-310qtl/acre.
COJ 64: Canes are of light yellow color and 2-2.5m long. This variety is resistant to lodging. Also this variety does not produce flowers. It is resistant to red rot. Gives average yield of 290-310qtl/acre.
Pratap Ganna-1 (COPK 05191): This variety is resistant to lodging, smut disease and drought conditions. It gives average yield of 335qtl/acre.
Co 1111: It is late duration variety. It is resistant to lodging, red rot and other pests. It gives average yield of 330-420qtl/acre.
CO 00421: Ready to harvest in 280-300days. Cane are medium size and of light green color.
COJ 97015: It is known for its medium maturing variety and gives high yield.
Other state varieties:
CoJ 85: It is early season variety. It is tolerant to red rot and frost. It is pronned to lodging hence do proper earthing up and propping. Gives Average Yield of 306quintal/acre.
CO 118: Early season variety. The canes of this variety are medium thick, greenish yellow color. It is tolerant to red rot and frost. It performs well under high fertility condition with frequent irrigation. Gives Average yield of 320qtl/acre.
CoH 119: Mid-season variety. It has tall thick greenish canes with prominent weather. It is tolerant to red rot and frost. It is an average ratooner. Gives Average yield of 340qtl/acre.
CoJ 88: Mid-season variety. Canes are tall with medium thickness and are of greyish color. Its juice contains 17-18% of sucrose. Ratoon yield is also excellent. It is non-lodging. And it is tolerant to red rot. Produces gur of good quality. Also suitable for saline irrigation water. Gives Average yield of 337qtl/acre.
CoS 8436: It is mid-season variety. It is short red variety with thick sturdy greenish yellow canes. It is non-lodging and tolerant to red rot. Gives excellent yield under high fertility soils with frequent irrigations. Gives average yield of 307qtl/acre.
CoJ 89: It is suitable for late planting. It is resistive to red rot, easy to detrash and non- lodging. It gives average yield is 326qtl/acre.
COH 110: It is late maturing variety.
CO 7717: Early maturing, high sugar content variety. It gives moderately resistant to red rot. Also having good juice content and maintaining this property for long period.
COH 128: Early maturing variety of sugarcane.
CoPb 93: The variety is red rot disease and frost tolerant. This variety contains 16-17% of sucrose in November and 18% of sucrose content in December. It gives an average cane yield of 335qtls/acre. It gives good quality of gur.
CoPb 94: This variety contains 16% of sucrose in November and 19% of sucrose content in December. It gives an average cane yield of 400qtls/acre.
Cos 91230: Gives average yield of 280qtl/acre.
Co Pant 90223: Gives average yield of 350qtl/acre.
CoH 92201: Early maturing variety, gives average yield of 300qtl/acre.
Cos 95255: Early maturing variety, gives average yield of 295qtl/acre.
CoS 94270: Gives average yield of 345qtl/acre.
CoH 119: Early maturing variety, gives average yield of 345qtl/acre.
Give two ploughings to land. First ploughing should be given at depth of 20-25cm depth. Crush clods with suitable implements or machine.
Time of sowing
planting season of sugarcane is mid-February to mid-march. Sugarcane takes generally one year to mature therefore called as Eksali.
Spacing
Use line to line spacing of 90cm for heavy and good cultivation and use 75cm for light and less cultivation.
Sowing Depth
Sow the sugarcane at a depth of 3-4 cm and cover it with soil.
Method of sowing
A)For sowing use improved method of planting like deep furrow, trench method, paired row method or ring pit method.
1) Dry planting in ridges and furrow: With the help of tractor drawn ridger, make ridges and furrows at distance of 90cm. Plant sugarcane setts then cover it with soil. After then give light irrigation.
2) Paired row planting: Make trenches at 150cm distance using trenches opener. Plant sugarcane in pairs row using 30:30-90-30:30cm spacing. It gives higher yield as compared to ridges and furrow.
3) Ring Pit method: Circular pits of 60cm diameters are dug at depth of 30cm with a tractor mounted digger. 60cm gap is provided between adjacent pits. 2-3 ratoons can be taken. 25-50% higher yield can be obtained compared to ridge and furrow.
B) Single budded set planting: Select healthy setts for plantation. Make furrows at distance of 75-90cm. Place single budded setts. If only small size setts from top portion of cane are selected then they are planted at distance of 6"-9". Place eye of sett on upward direction to ensure proper and quick germination. Cover setts with soil and apply light irrigation.
Seed Rate
Various research and experiment shows that, germination percentage of 3 bud sets is higher than the setts having more or less than three buds. Germination percentage of single bud sett is very low because of moisture loss from other cut end. Also if whole can stalk is planted without giving any cut, still germination percentage remain low as only top end will get germinate.
Seed rate vary from region to region. In North West India, seed rate is high because of low germination percentage and adverse weather i.e. hot weather with desiccating winds. Use seed rate of 27,500-27,800 for two budded sets per acre and 16,500-18,750 for three budded setts per acre.
Seed Treatment
Take seed material from crop of 6-7months age. It should be free from pest and disease. Discard pest, disease affected and damaged buds and canes. Treat seed crop one day before planting, it will give high and uniform germination. The setts should be soaked in Carbendazim@1gm in 1litre of water. After chemical treatment, treat seeds with Azospirillum. For that dip setts in Azospirillum inoculum@800gm/acre +sufficient water solution for 15min before planting.
Soil Treatment
Suspended 5 kg of bio fertilizer per acre in 10 liters of water & mixed with thoroughly with 80-100 kg of FYM. The mixed bio fertilizer in FYM is sprinkled over cane setts in the rows at the time of planting. Immediately rows should be covered.
In sugarcane due to weed infestation about 12 to 72% yield loss is observed depending upon severity. Initial 60-120 days are critical for weed management. Therefore weed management practices should be adopt within 3-4 months after planting. For control of weeds, chemical is not only solution. Adopting mechanical as well as cultural practices gives effective solution.
1) Mechanical Measure: As sugarcane is widely space crop, weeding with hand or intercultural operation can be easily carried out. Take 3-4 hoeings after every irrigation.
2) Cultural Operations: It included change in cropping pattern, intercropping and trash mulching. Monocropping leads to heavy infestation of weed. Crop rotation with fodder or green manure crops suppresses weeds. Also sugarcane is wider space crop so there is opportunity for weed to grow in large numbers. If sugarcane is intercrop with short duration crops then it will suppress the weed growth also give additional benefit. In trash mulching, mulch of 10-12cm thickness is provided in between cane row after emergence of cane. It will restrict the sunlight thus help to check weed growth. It also conserved soil moisture.
3) Chemical: To control weeds, carry out pre-emergence weedicide application with Simazine or Atrazine@600-800 g/acre or Metribuzin@800 g/acre or Diuron@1- 1.2 kg/acre. Apply pre-emergence herbicides immediately after planting. Apply 2,4-D@300-400 g/acre as post-emergence herbicide for broad-spectrum weed control in sugarcane.

Early shoot borer: Attacked in germination stage upto internodes formations. Larva makes holes in shoot below the ground level and then enter into it thus causes dead heart. It gives offensive smell. It is mostly observed in light soil and in dry weather. Pest is active from March - June.
Avoid late plantation. Apply Chlorpyriphos@1litres/acre with 100-150 litres of water over the setts placed on furrows with the help of rosecan. Remove dead heart infected plants. Give light irrigation and avoid drying of field.
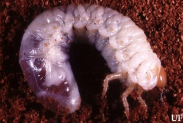
White Grub: These feed on root system and thus damage to crop. Entire drying up of stalks and easily dislodging of cane are main symptoms for white grub infestation. In initial stage infestation observed in patches and afterwards it spread on entire field.
The adult beetles emerge from the soil during June-July with the first showers of rain. They congregate on the nearby trees and feed on their leaves during night. The eggs are laid in the soil and the larvae (grubs) hatching from them eat away the rootlets or root hairs of the groundnut plants. To destroy beetles spray Imidacloprid@4ml/10Ltr of water on trees of nearby sugarcane trees.
For effective management of white grub. Plough the field and exposes the beetles resting in the soil. Do not delay crop sowing. Before sowing treat cane with Chlorpyriphos. Apply Phorate@4kg or carbofuran@13kg per acre in the soil at or before sowing. In heavily infested fields, flooding is to be done for 48 hrs. Do drenching of Clothianidin@40gm/acre with 400 Ltr of water using cane.

Termite: Before sowing do cane treatment. Dip setts in imidacloprid solution@4ml/10Ltr for 2min or at time planting spray Chlorpyriphos@2litre/acre on setts.
If infestation occur in standing crop, drench with Imidacloprid@60ml/150litre of water or Chlorpyriphos@1ltr/200Ltr of water.

Pyrilla: Severe pest of north India. Adult suck leaf sap under the surface of leaves. It results in yellowing white spot and withering. They secretes honey like substance and attract sooty mould fungi, due to this leaves become blackish.
At regular interval, collect and destroy white-puffy egg masses. In severe infestation spray with Dimethoate@2ml/ltr or Acephate@800gml/150Ltr of water.

Root borer: Borer enter into root zone of shoot below ground. Infestation is high from July onward. Due to infestation yellowing of leaves from leaf apex to downwards along the margin is seen.
Before sowing do cane treatment with Chlorpyriphos. In dry field infestation is low so keep field dry and clean, avoid water logging condition in field. Carry out earthing operation at 90days. If infestation is observed in field, do drenching with Chlorpyriphos 20EC@1Ltr/acre with 100-150Ltr of water near the root zone or do granular application of Quinalphos@300ml/acre. Remove infected cane and destroyed it away from field.

Stalk Borer: It is active from July onwards with onset of monsoon. Larvae feeds on inner surface of leaf sheath, mid rib and stalk. It can attack any region of stalk. Infestation continues from cane formation to harvest.
Avoid excess use of nitrogen, keep field clean and provide proper drainage. Provide earthing up to prevent crop from lodging. Chemical control is rarely effective. Release parasitoid, Cotesia flavipes@800 mated females/acre at weekly interval from July to November.

Top Borer: It attacks crops from tillering to maturity phase. Larvae makes tunnels into midribs causes white streak which later turns brown. If infestation occurs during tillering phase, the attacked shoots dies resulting in dead heart formation. If it attacks on grown up canes, apical growth is arrested resulting in bunchy top symptoms.
To control do drenching of Rynaxypyr 20SC@60ml/acre in 100-150Ltr of water in between period of month end of April to first week of May. Maintain proper drainage in soil, as water logging increases top borer incidence.

Red Rot: From top, third and fourth leaves show yellowing and drying. At later stage show discolored lesion on rind. If split the diseased stalk show reddening of internal tissue. A sour and alcoholic smell emanates from the infected cane.
To control grow disease resistance varieties. Select disease free cane for sowing. Discard cane which show reddening at cut end and at the nodal region. Do crop rotation with paddy or with green manure crops. Avoid water logging field. If infestation is observed remove the crop and destroyed it away from field. Disinfect soil around the diseased clump with Carbendazim@400gm/150ltr per acre.

Wilt: Root borer, nematodes, termite, drought and water logging condition cause plant to wilt infection. Crown leaves turn yellow and loose turgor and withers. Boat shape cavities appears in pith region and crop get shrink. It reduces germination and reduces yield.
Use disease free setts for planting. Do setts treatments with Carbendazim@0.2% + Boric acid@0.2% for 10min. Intercropping with onion, garlic and coriander will reduces the wilt disease.

Pokkah Boeng: It is air borne disease. Symptoms are observed in monsoon. Disease plant bear distorted and wrinkled leaves. Leaves show reddish patches at base of leaf blade. Newly formed leaves become shortened and sword like.
Grow Pokkah boeng disease resistive varieties. If infection of disease is observed spray with Carbendazim@4gm/Ltr or Copper Oxychloride@3gm/Ltr or Mancozeb@3gm/Ltr of water.
Harvesting of cane at right time is necessary for good yield and for high sugar recovery. Harvesting at over aged or under aged cane leads to loss in cane yield. Depending upon withering of leaves and cane juice, harvesting time can be decided. To know the right harvesting time some farmer used hand sugar refractometer is used. Sickles are used for harvesting. Stalks are cut at ground level so that the bottom sugar rich internodes are harvested which add to yield and sugar. De-topping at appropriate height. After harvesting quick disposal of the harvested cane to factory is necessary.
Sugarcane provides a juice, which is used for making white sugar, and jaggery (gur) and many by products like bagasse and molasses.
Sugarcane, Saccharum officinarum L. is a perennial grass. It belongs to bamboo family and it is indigenous to India. It is the main source of sugar, gur and khandsari. About two-thirds of the total sugarcane produced in India is consumed for making gur and khandsari and only one third of it goes to sugar factories. It also provides raw material for manufacturing alcohol. Brazil is largest producer of sugarcane followed by India, China, Thailand, Pakistan and Mexico. In India, Maharashtra is largest producer of sugar and it contributes about 34% of sugar in country followed by Uttar Pradesh. In Rajasthan, sugarcane is cultivated in districts like Ajmer, Jaipur, Dausa etc. Under irrigated conditions it gives good results.
You have successfully login.
Your email and password is incorrect!