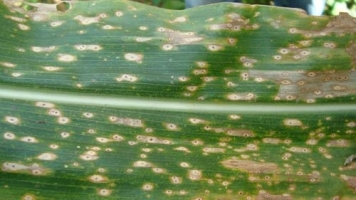
Rajasthan has the largest area for maize production in India. It has around 1 million ha of area for maize cultivation with production of 1.1 million tonnes and the productivity of 450-460 kg/acre. Rabi maize i.e. in winter’s crops is cultivated in absolutely sure irrigated conditions. It is mainly used in India as a food crops and productivity is increased by planting early maturing hybrid varieties and improved composite varieties. By growing quality protein maize, it will help to increase the protein level in food and feed. In Rajasthan, the productivity of maize is low due to non-availability of hybrid varieties such as early maturing or drought tolerant varieties and hybrid seeds. Incidence of downy mildew disease is a major concern.
By growing maize, farmers can easily shield the deteriorating grade of soil, preserve 90% of water and 70% of potency as compared with paddy and can make more profit than wheat and paddy, reported by vice chancellor, Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana. It serves as basic raw material to thousands of industrial products like oil, starch, alcoholic beverages etc. Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Bihar, Himachal Pradesh, J & K and Punjab are major maize growing states. AP and Karnataka is major producer of maize in south.