Organic Details
Basic way of organic farming
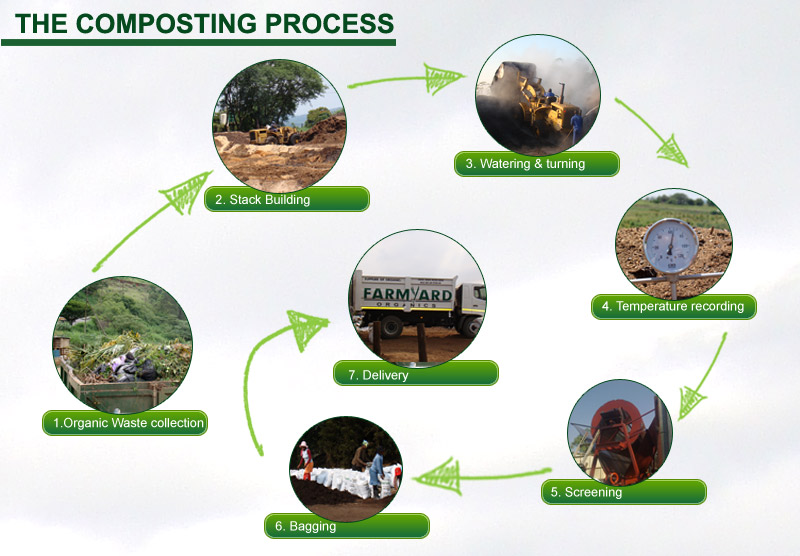
Plenty rotted natural material produced from trash is known as compost. Composting is the procedure of 'rotting' and decomposition of natural material by microbes under managed factors. Fresh natural components like plant residues, livestock waste materials, meal trash, certain municipal debris as well as desirable manufacturing wastes, improve their capability for utilization to the ground just like a fertilizing source, after possessing composting.
Garden compost is an excellent way to obtain organic and natural material. Land natural matter performs a significant role in maintaining soil fertility, so in endurable farming generation. Except for being a supply of crop nutrition, it enhances the physico-chemical as well as standard elements of the land. Due to such upgrades, the land:
(i) turns into extra resilient against challenges like drought, disorders as well as toxins;
(ii) assists the plants in enhanced uptake of crop nutritional value;
(iii) offers a potent nutritional cycling ability due to vital microbial action.
Such benefits emerge their way in lowered cropping hazards, better crops as well as reduced outlays on inorganic fertilizers for farmers. The regular nutritional elements of garden compost are 0.15% P2O5, 0.5% N and 0.5% K2O.
Why Composting
The discarded organic substances consist of highly developed chemical substances like cellulose, lignin, lipids, hemicellulose, proteins, polysaccharides and so on. All these highly developed components could not be utilized not as resource elements. They must be transformed into uncomplicated inorganic component like existing nutrition. The substance placed into soil without transformation can acquire transformation inside the land. This transformation procedure eradicate lot of power as well as accessible nutrition from the land disturbing the plants. Thus transformation interval is compulsory.
Crop rotation
Considered one of the of beneficial organic farming is crop rotation in which crops are rotated from 1 to next season, thus similar crops are not grown in an exact area, instead of frequently grown, plant it after 3 yrs. The aim of crop rotation is simply to manage the stability of organic matter, microbes as well as nutrition essential for well-balanced soil. Out of the three the soil-dwelling microbes are best output of crop rotation. Crop rotations even block the accumulation of bugs as well as infections, that help organic farmers to prevent the utilization of chemical pesticides.
Organic farmers sow alternating sets of crops (cereals, roots, legumes, brassicas) to bring fertility as well as to reduce bugs and disease problems. Certain crops, such as clover, provide nutrition to the land – although wheat as well as potatoes consume nutrition. Rotations usually include a ‘rest’ time period for particular areas, in which ‘green manure’ like clover is grown for a certain period, before getting grazed or even ploughed into the land to contribute fertility. This can be referred as sowing a ‘ley’.


