-
Rainfall
75-200cm -
Temperature
20-25°C -
Sowing Temperature
22-25°C -
Harvesting Temperature
24-28°C
Agriculture

General Information
Citrus is an important fruit crop. Lime is one of them. It is mainly known for its pulp and juice throughout the world. Different citrus fruits are used throughout the world as food or juice. In central India, Nagpur santra is grown on a large scale. Mandarin Production states are Assam, Dibrugarh and Brahmaputra valley. In India Citrus cultivation is done on an area of about 923 thousand hectare with annual production of 8608 thousand metric tons.
Climate
-
Rainfall
75-200cm -
Temperature
20-25°C -
Sowing Temperature
22-25°C -
Harvesting Temperature
24-28°C
-
Rainfall
75-200cm -
Temperature
20-25°C -
Sowing Temperature
22-25°C -
Harvesting Temperature
24-28°C
-
Rainfall
75-200cm -
Temperature
20-25°C -
Sowing Temperature
22-25°C -
Harvesting Temperature
24-28°C
Soil
Citrus can grow in all types of soils. Light Soils having good drainage are suitable for its cultivation. pH range of soil should be 5.5-7.5. They can also grow in slightly alkaline and acidic soils. Light loam well drained soils are best for citrus cultivation.
Popular Varieties With Their Yield
Hill Ideal: Plant grow up to height of 55-60cm. Ready for first picking in 80days after transplantation. Sprouts are light green, globular and solid. It gives average yield of 40-65qtl/acre.
Other state varieties:
Jade cross: Early duration, high yielding hybrid. Suitable for single harvest. Ready for picking in 85days after transplantation. Sprouts are medium size.
Rubine: High yielding variety.
Bubbles: Ready to harvest in 90days after transplantation. Suitable for long harvest.
Other varieties: Abacus, Maximus, Cronus, Diablo,
Dwarf variety: Improved long island, dwarf improved, Early Morn
Tall variety: Red vein, Amager.
Land Preparation
Land should be ploughed, cross ploughed and leveled properly. Planting is done on terraces against slopes in hilly areas. High density planting is also possible in such areas.
Sowing
TIME OF SOWING
Sowing is done in February-March month and June-July month.
INTERCROPPING: Intercropping with Cow peas, Vegetables, French beans can be done in initial two to three years.
SPACING
Spacing between plants should be kept between 6m X 6m.
SOWING DEPTH
Pits of size 60×60×60cm should be dug for planting seedlings.
METHOD OF SOWING
Propagation
Plants are propagated by budding or Air layering.
Fertilizer
Fertilizer Requirement (gm/tree)
| UREA | SSP | MOP |
| 50 | 50 | 50 |
Application of Urea@50gm/tree, SSP@50gm/tree and MOP@50gm/tree should be given per year. Along with these, use of zinc sulphate should be done in April, June and September month. Half dose of nitrogen and potash is given in February-March month and rest of the dose is given in the June-July month. Complete dose of phosphorus is given in spring season before 20 days of plant growth.
Seed
SEED RATE
Minimum plant density of 111 Plants/acre should be maintained.
Pruning and Training
For proper growth of trunk of plant, shoots in 50-60cm near ground level should be removed. Centre of plant should remain open. Water suckers should be removed at early stages of growth.
Weed Control
Weed can be controlled by hand-hoeing and also controlled by chemically, use glyphosate@1.6litre per 150 litre of water. Use glyphosate only on weeds not on crop plants.
Irrigation
Lime requires irrigation at regular intervals. Lifesaving irrigation should be given in winters and summers. Irrigation is necessary for Flowering, Fruiting and proper plant growth. Over irrigation may also lead to diseases like root rot and collar rot. High frequency irrigation is beneficial. Salty water is injurious for crop plants. Partial drying out of soil in spring may not affect plants.
Plant protection
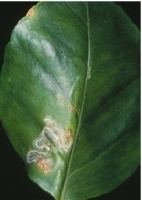
- Pest and their control:
Leaf miner: Larvae inside the upper or lower surface of young and newly emerged leaves are curled and look distorted. Young trees show a reduction in growth due to leaf miner. Best management for leaf miner is to leave it alone and let the natural enemies to feed upon them and parasitize their larvae. It can also be controlled by spraying Phosphomidon @1ml or Monocrotophos @1.5ml per 3-4 times fortnightly. Pheromone traps are also available for detecting leaf minor moths.

Citrus Psylla: These are Juice sucking pests. Damage is mainly caused by Nymphs. It injects a plant toxin liquid which burns foliage and skin of fruit. Leaves curl and fall off prematurely. It can be controlled by pruning of diseased plants, burning them. Spraying of Monocrotophos-0.025% or carbaryl- 0.1% can also be helpful.

Scale Insects: Citrus scale insects are small insects that suck sap from the citrus trees and fruits. Honeydew is produced which is feasted upon by ants. They do not have much mouth parts. Male citrus scale has a short life span. There are mainly two types of scale on citrus plants armored scale and soft scales. Armored scale insects insert their mouth parts in the plant and never move again, eating and reproducing in the same spot. Soft scale bugs on citrus form a protective coating, which in turns cover citrus leaves and prevents photosynthesis. Once dead, soft scale will fall from tree instead of remaining stuck. They can be controlled with the introduction of indigenous parasitic wasps. Neem oil is also effective against them. Spraying of Parathion (0.03%) emulsion, dimethoate 150ml or malathion @0.1% are effective against scale control.

Aphids & Mealy Bugs: They are small sap sucking pests. Bugs are present on the underside of leaves. Synthetic pyritheriods or pest oil can be used to control aphids and bugs.

- Disease and their control:
Citrus Canker: Plants have lesions on stems, leaves and fruits with brown, water-soaked margins. Citrus canker bacteria can enter through plant’s stomata into the leaves. Younger leaves are highly susceptible. Lesions oozes bacterial cells which can be dispersed by blowing wind to healthy plants in area.
Contaminated equipment tends to spread disease to healthy plants. Bacteria can stay viable in old lesions for several months. It can be detected by appearance of lesions. It can be controlled by cutting of effected branches, twigs. Spraying of Bordeaux mixture @1%. Aqueous solution of 550ppm, Streptomycin Sulphate is also helpful in controlling citrus canker.

Gummosis: Exudation of gum from bark of tree is the characteristic symptom of gummosis disease. Affected plant leaves turns to pale yellow in color. Hardness masses of gum are common on stem and leaf surfaces. In severe cases, bark may be destroyed by rotting and tree may dies. Plant dies before the fruit matures. This disease is also called foot rot. This disease can be managed through proper selection of site with proper drainage, use of resistant varieties etc. Plant injuries should be avoided. Drench the soil with 0.2% metalaxyl MZ-72 + 0.5% trichoderma viride, which helps to control this disease. Bordeaux mixture should be applied to plant upto 50-75 cm height from ground level at least once in a year.

Powdery mildew: White cottony powdery growth is noticed on all aerial plant parts. Leaves tend to become pale yellow and crinkle. Distorted margins are also seen. Upper surface of leaves are more affected. Young fruits drop off prematurely. Yield is reduced significantly. To control powdery mildew, affected plant parts should be removed and destroyed completely. Carbendazim, three times at 20-22 days of interval helps to control this disease.
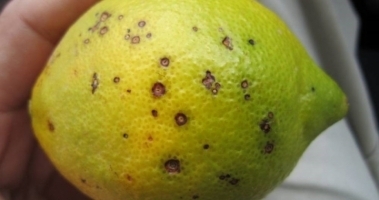
Black Spot: Black spot is a fungal disease. Circular, dark spots on fruits are seen. Copper spray in early spring should be sprayed on foliage helps to cure plants from black spots. It should be repeated in 6 weeks again.

Collar Rot: Collar rot is also caused due to fungus. This disease mainly affects the bark on tree trunk. Bark begins to rot and forms a band just above ground surface, this band decay gradually and covers the whole trunk. It is very severe in some cases that even the trees may die. This is caused due to incorrect mulching, injury due to weeding, mowing etc. Tree may lose its vigor. To protect trees from collar rot, cut and scrape away the soft, infected bark to clean the trunk of tree. Mixture of copper spray or Bordeaux mixture should be painted on the affected part of the tree. Remove all the weak, diseased and congested tree branches to ensure proper air circulation.

Zinc Deficiency: It is very common in citrus trees. It is notified as yellow areas between main lateral veins and midrib of the leaves. Twigs may die back, dense shoots having stunted bushy appearance is commonly seen. Fruits tend to become pale, elongated and small in size. Proper fertilizer application should be given to the citrus tree to prevent zinc deficiency. Zinc sulphate should be provided by dissolving 2 table spoons in 10 liters of water. This should be sprayed thoroughly on all the tree branches and foliage. It can also be cured by providing cow or sheep manure.

Iron deficiency: Color of new leaves changes to yellowish green. Iron chelates should be provided to the plants. Cow or Sheep manure is also helpful to cure plants from iron deficiency. This deficiency mostly occurs in case of alkaline soils.
Harvesting
On attaining proper size, shape along with attractive color having TSS to Acid ratio of 12:1, lime fruits is ready for harvest. Depending upon variety fruits are generally ready for harvesting in Mid- January to Mid- February. Do harvesting at proper time as too early or too late harvesting will give poor quality.
Post-Harvest
After harvesting, wash fruits with clean water then dip fruits in Chlorinated water@2.5ml per Liter water and then partially dried them. To improve appearance along with to maintain good quality, do Citrashine wax coating along with foam. Then these fruits are dried under shade and then packing is done. Fruits are packed in boxes.










