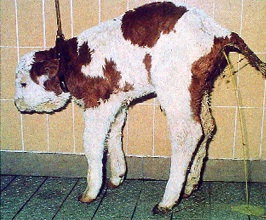
 Diseases of digestive system:
Diseases of digestive system:
Treatment of simple indigestion:
• Provide them feed which gets digested easily.
• Give them spices which will help to increase hunger.
Treatment of acidic indigestion:
• Avoid giving acidic fodder to animals.
• During the start of disease, give animals’ saline elements such as baking soda etc. and medicines which will help to give energy to liver.
Treatment of saline indigestion:
• During preliminary disease, give light acid such as 5% acetic acid @5-10ml per animal weight or approximately 750ml vinegar to cure the disease.
• If brain stroke is occurring and no difference is seen after giving medicine 2-3 times, then rumenotomy operation should be done by doctor.
Treatment of constipation:
• In starting give them flax oil@500 ml and don’t give them dry fodder as a feed and give them more amount of water.
• For large animals, solution of Magnesium sulphate@800gm and scrape of ginger powder@30gm is given to animals through mouth.
Treatment of acidity:
• Turpentine oil@30-60ml, extract of Asafetida (heeng)@60ml or mustard/flax oil@500ml is given to animals (don’t give too much amount of Turpentine oil, this will lead to stomach issues).
• If this disease is seen again and again in animal, then activated charcoal, 40% Formalin@15-30ml and Dettol water should be given.
• Look at the type of disease and the condition of the animal, consult the vet.
Treatment of bloody diarrhea:
• Give sulpha medicines through mouth or vaccinations and along with this give more amount of Glucose@5% and water.
• Antibiotic, Sulpha medicines and opiate, tennoform or iron elements can also be given to get rid from diarrhea.
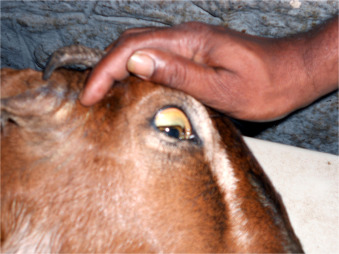 Jaundice:
Jaundice:
Types of Jaundice:
1. Pre hepatic or hemolytic jaundice- due to destruction of red blood cells.
2. Intra hepatic or poisonous jaundice- due to liver disease
3. Jaundice due to closure of lymph nerves
Treatment:
• First of all find out the cause of poisonous jaundice and then remove it.
• The animals that have infection and blood pest diseases, take away those animals from other animals.
• Give glucose and salt solution, calcium gluconate solution, Vitamin A and C and along with this give antibiotic medicines.
• Give animals liver tonic along with green fodder and fatless feed.
• During the deficiency of phosphorus, give animals’ sodium acid monophosphate.
 Anthrax: It is an extremely infectious as well as deadly disorder of cattle’s due to spore-forming rectangular structured bacterium referred as Bacillus anthracis. Anthrax is common in every region, leads to severe mortality in ruminants. The microbe generates incredibly strong toxins that are the cause of the bad impacts, leading to large number mortality. The microbe generates spores on exposure with air. Symptoms of the disease generally emerge in 4 to 7 days after the spores are either inhaled or ingested. As symptoms start appearing in animals, they often expire within a couple of days. They typically obtain the illness by ingesting anthrax spores when grazing on pasture infected with anthrax spores. Breathing the spores, that are colourless, odourless, even tasteless, can also induce infection in human as well as animals.
Anthrax: It is an extremely infectious as well as deadly disorder of cattle’s due to spore-forming rectangular structured bacterium referred as Bacillus anthracis. Anthrax is common in every region, leads to severe mortality in ruminants. The microbe generates incredibly strong toxins that are the cause of the bad impacts, leading to large number mortality. The microbe generates spores on exposure with air. Symptoms of the disease generally emerge in 4 to 7 days after the spores are either inhaled or ingested. As symptoms start appearing in animals, they often expire within a couple of days. They typically obtain the illness by ingesting anthrax spores when grazing on pasture infected with anthrax spores. Breathing the spores, that are colourless, odourless, even tasteless, can also induce infection in human as well as animals.
Treatment: Treatment can be done only in sub-acute form of illness. They can be treated in early stage only. The antibiotics used for their treatment are Ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, tetracycline and penicillin.
 Anaplasmosis: It is an infectious disease which is caused by Anaplasma marginale. Its symptoms are increased body temperature, nasal discharge, coughing, grinding of teeth, inappetance, pale and icteric mucous membrane.
Anaplasmosis: It is an infectious disease which is caused by Anaplasma marginale. Its symptoms are increased body temperature, nasal discharge, coughing, grinding of teeth, inappetance, pale and icteric mucous membrane.
Treatment: Spraying or dipping of acaricidal medicine to control the insect population. Serological test is done to check the anaplasmosis disease. If the result is positive then immediate treatment is given by qualified veterinary doctor.
 Anemia: The symptoms are muscular weakness, depression, anorexia and increased heat rate. The disease is caused due to poor nutrition management, inadequate nutrients in diet and colostrum intake.
Anemia: The symptoms are muscular weakness, depression, anorexia and increased heat rate. The disease is caused due to poor nutrition management, inadequate nutrients in diet and colostrum intake.
Treatment: Vitamins A, B and E is given in the diet and injection of iron dextrin @150mg is given to cure the anaemia.
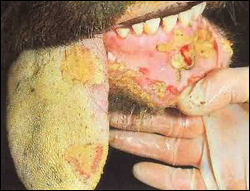 Foot-and-mouth: The disorder is an extremely communicable influencing cloven-footed pets or animals. This is indicated by fever, growth of vesicles as well as blisters in the udder, oral, teats and even on the dermis between the paws also above the hoofs. Mammals restored from the disorder display a specifically irregular covering as well as deformation of the hoof. In India, this disorder is prevalent. The infection develops by straight communication even indirectly from contaminated manure, fluid, and hay. It can also be transferred by cattle attendants. Sometime it can spread via retrieved livestock or by birds. High temperature, hanging saliva, lameness is seen.
Foot-and-mouth: The disorder is an extremely communicable influencing cloven-footed pets or animals. This is indicated by fever, growth of vesicles as well as blisters in the udder, oral, teats and even on the dermis between the paws also above the hoofs. Mammals restored from the disorder display a specifically irregular covering as well as deformation of the hoof. In India, this disorder is prevalent. The infection develops by straight communication even indirectly from contaminated manure, fluid, and hay. It can also be transferred by cattle attendants. Sometime it can spread via retrieved livestock or by birds. High temperature, hanging saliva, lameness is seen.
Treatment: Apply antiseptics for healing ulcers. For the feet lesion use copper sulphate and coal tar in 5:1 proportion. Recommended vaccines should be given. Proper care of sanitized vesicles should be used to control the files and spore.
 Hypomagnesaemia: The symptoms are continuous movement of ears, hyper-excitement, Incoordination of gait, loss of urination etc. the disease is mainly caused when calves are fed only on milk.
Hypomagnesaemia: The symptoms are continuous movement of ears, hyper-excitement, Incoordination of gait, loss of urination etc. the disease is mainly caused when calves are fed only on milk.
Treatment: Magnesium oxide @5g or magnesium carbonate @8g is added in the diet to get rid of hypomagnesaemia.
 Lead poisoning: Sunken abdominal pain and calf is dull are the major symptoms of lead poisoning. It mainly occurs when they lick the metalwork, painted tarpaulins, lead batteries etc.
Lead poisoning: Sunken abdominal pain and calf is dull are the major symptoms of lead poisoning. It mainly occurs when they lick the metalwork, painted tarpaulins, lead batteries etc.
Treatment: Dose of calcium versenate @25% twice a day is given to cure the lead poisoning in sub-acute cases.
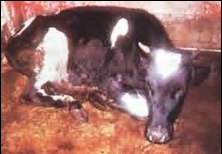 Rinderpest: This is one of dangerous viral strain of livestock. Some time ago there was no control, but organized efforts have brought a total elimination of the disorder in Western Hemisphere. The disorder even now endures in the Asian regions. The virus is located remarkable in the saliva; withdraw from eye sight as well as from nose, even in the feces as well as urine. They are within the circulating bloodstream throughout the febrile period and afterward target to several body parts, specifically in the liver, lymph nodes as well as spleen. They are demolished by direct sun rays as well as disinfectants outside the body. Cold conditions sustain this viral infection. The virus is generally spread by polluted food and fluid. Show increased body temp about 104 – 107oF. Lacrimation as well as itchiness of eyes is some of its symptoms. Unpleasant odour comes from oral cavity. Bloody mucoid diarrhea is discovered.
Rinderpest: This is one of dangerous viral strain of livestock. Some time ago there was no control, but organized efforts have brought a total elimination of the disorder in Western Hemisphere. The disorder even now endures in the Asian regions. The virus is located remarkable in the saliva; withdraw from eye sight as well as from nose, even in the feces as well as urine. They are within the circulating bloodstream throughout the febrile period and afterward target to several body parts, specifically in the liver, lymph nodes as well as spleen. They are demolished by direct sun rays as well as disinfectants outside the body. Cold conditions sustain this viral infection. The virus is generally spread by polluted food and fluid. Show increased body temp about 104 – 107oF. Lacrimation as well as itchiness of eyes is some of its symptoms. Unpleasant odour comes from oral cavity. Bloody mucoid diarrhea is discovered.
Treatment: It can be treated with sulphadimidine, streptomycin or penicillin but when they are controlled on primary level.
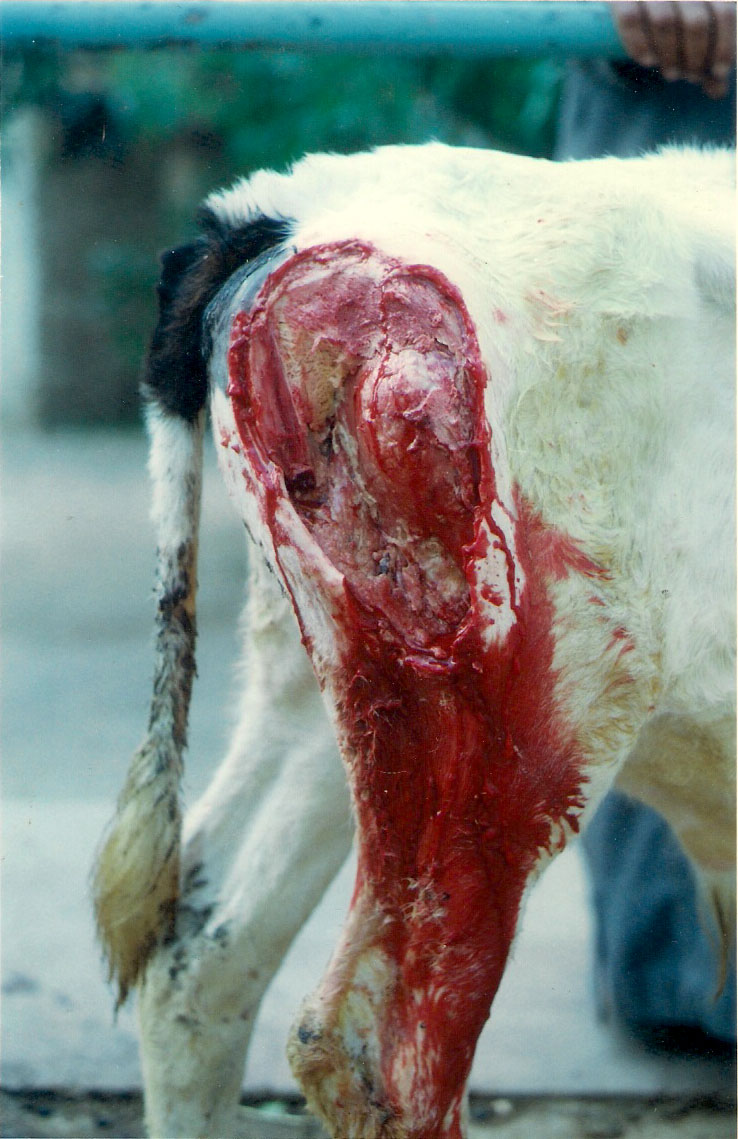 Black Quarter: This bacterial infection is a severe infection with lethal effects on livestock. Cattle are mostly infected in the young age of 6-24 months. These are sporadic infection mainly born from soil during rainy season. The animal suffer from high fever, difficulty in breathing. Loss of appetite, dullness. High pulse and heart rate.
Black Quarter: This bacterial infection is a severe infection with lethal effects on livestock. Cattle are mostly infected in the young age of 6-24 months. These are sporadic infection mainly born from soil during rainy season. The animal suffer from high fever, difficulty in breathing. Loss of appetite, dullness. High pulse and heart rate.
Treatment:
1) High dose of Oxytetracycline i.e. 5-10 mg/Kg body weight 1M or IV.
2) Injection of Avil / Cadistin @ 5-10 ml IM.
3) Penicillin @ 10,000 units /Kg body weight 1M & locally daily for 5-6 days.
4) B.Q. antiserum in large does.
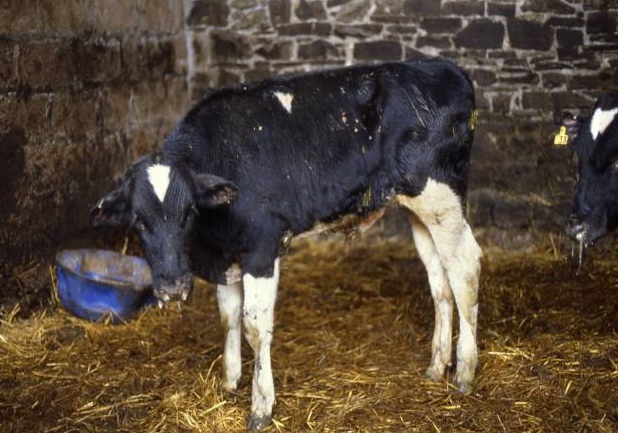 Calf pneumonia/ Enzootic bronchitis: The calf pneumonia is mainly caused by wet floors or beddings. It is caused by infectious agents such as Parainfluenza herpesrvirus, Pasteurella, Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus (BRSV), Mycoplasma etc. and can also be infected by the contact with infected animal.
Calf pneumonia/ Enzootic bronchitis: The calf pneumonia is mainly caused by wet floors or beddings. It is caused by infectious agents such as Parainfluenza herpesrvirus, Pasteurella, Bovine Respiratory Syncytial Virus (BRSV), Mycoplasma etc. and can also be infected by the contact with infected animal.
Treatment: Proper dry bedding and proper ventilation is required.
 Enteritis/ Diarrhoea/ Calf scours: In this disease first the excessive loss of water occur then acidosis and dehydration and then death of the animal. The disease mainly occurs due to unclean hygiene conditions, drinking unclean water and poor feeding systems.
Enteritis/ Diarrhoea/ Calf scours: In this disease first the excessive loss of water occur then acidosis and dehydration and then death of the animal. The disease mainly occurs due to unclean hygiene conditions, drinking unclean water and poor feeding systems.
Treatment: Clean the hygiene conditions. Treat with nitrofurazone @20mg/kg or with trimethoprim and sulphadoxin to cure from disease.
 Ectoparasites: The symptoms are itching, excitement, irritation and abscesses on skin. The disease is mainly caused by unclean surroundings and wet living conditions.
Ectoparasites: The symptoms are itching, excitement, irritation and abscesses on skin. The disease is mainly caused by unclean surroundings and wet living conditions.
Treatment: Application of coconut/peanut oil (3:1) mixed in Sulphur is used to cure disease.
 Endoparasites: The symptoms are diarrhoea, bottle jaw, listlessness etc. the disease is caused mainly because of unhealthy surroundings and ingestion of gates, licking of walls, infested floors etc.
Endoparasites: The symptoms are diarrhoea, bottle jaw, listlessness etc. the disease is caused mainly because of unhealthy surroundings and ingestion of gates, licking of walls, infested floors etc.
Treatment: Give clean drinking water. Deworming is required firstly at 2 weeks and then at the interval of 6 months. Dose of sulphamethazine/sulphadimidine is given to cure disease.
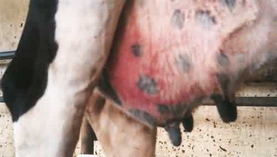 Mastitis: This disease the inflammation of mammary gland and is significantly lethal disease of livestock in worldwide. Though pressure or external wounds stimulates swelling of the gland, contamination by invading microbes (yeasts, fungi and even viruses) are the major source of mastitis. Diseases activate once the microbes permeate the teat canal then distribute in the mammary gland.
Mastitis: This disease the inflammation of mammary gland and is significantly lethal disease of livestock in worldwide. Though pressure or external wounds stimulates swelling of the gland, contamination by invading microbes (yeasts, fungi and even viruses) are the major source of mastitis. Diseases activate once the microbes permeate the teat canal then distribute in the mammary gland.
Treatment: Mastitis can be controlled by dipping the teat in germicide after each milking. Heifers are given antibiotic treatment while gestation. Drugs such as gramicidin, Tyrothricin and acriflavine are the effective drugs. Penicillin, sulphonamides and streptomycin are few other effective drugs used for its treatment.
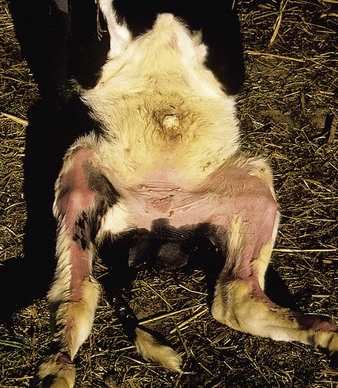 Navel-ill: The symptoms are loss of appetite, swollen and painful hock and knee joints, elevated temperature and infection in liver. It is generally caused by using unhygienic knife/blade and improper dressing of navel.
Navel-ill: The symptoms are loss of appetite, swollen and painful hock and knee joints, elevated temperature and infection in liver. It is generally caused by using unhygienic knife/blade and improper dressing of navel.
Treatment: Do proper dressing of navel cord and if external injury is seen, do proper dressing.
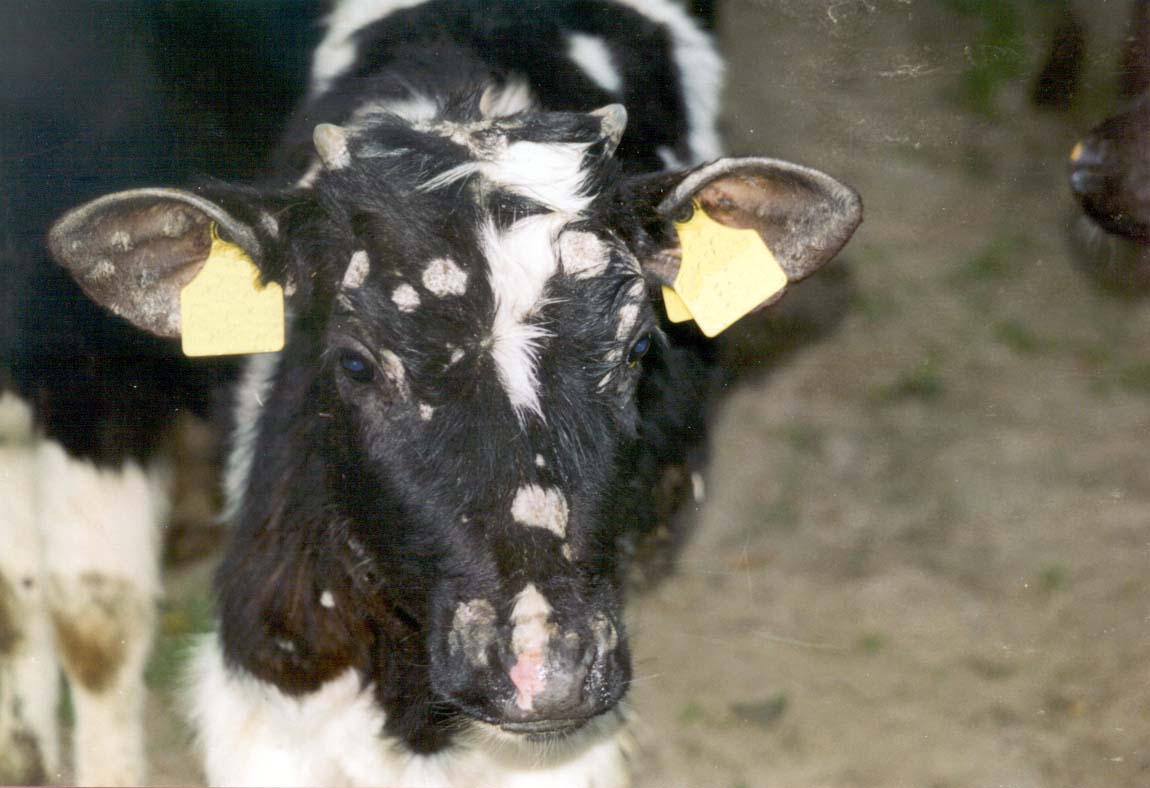 Ring worm: It is the most common skin infectious infecting beef cattle. This is a fungus infection, which is transmissible to humans also. Generally the infection emerges as crusty grey spots often around the head as well as collar and even around the eyes.
Ring worm: It is the most common skin infectious infecting beef cattle. This is a fungus infection, which is transmissible to humans also. Generally the infection emerges as crusty grey spots often around the head as well as collar and even around the eyes.
Treatment: As an initial step in managing the infection is, if possible, infected animals needs to be segregated as well as their pens even stalls cleaned up with disinfected. Wash the cattle which were infected with the infection, need to be attended thoroughly for the presence of scars as well as handled instantly. Adequate nourishment, especially excessive levels of Vitamin A, copper as well as zinc, aids to boost the stability of the animal. Communicate with the veterinarian as well as hook-up to shops for items to cure this infection. Applying a wormer such as Ivomec can destroy lice as well as assist in preventing cattle from itching which cause a skin injury due to which fungi can penetrate in.
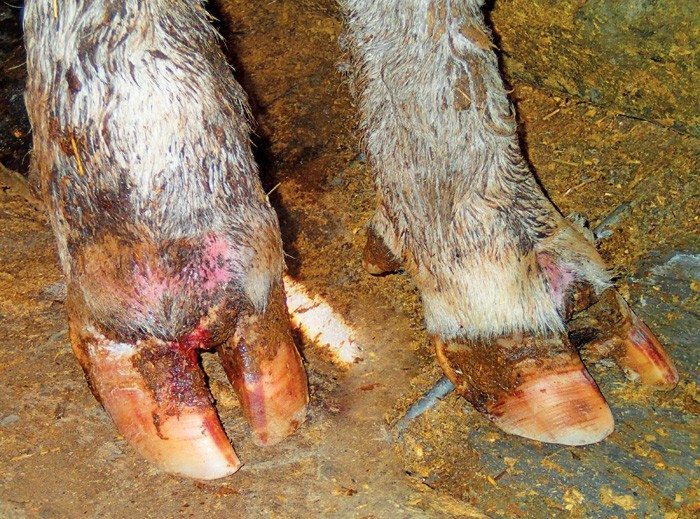 Foot rot: Foot rot is a basic source of lameness in cattle as well as develops most often while cattle are on pasture and enforced to move from slush to acquire water as well as food. Foot rot is stimulated while a cut rather scrape on the skin that permits disease to go through between the claws as well around the upper of the hoof.
Foot rot: Foot rot is a basic source of lameness in cattle as well as develops most often while cattle are on pasture and enforced to move from slush to acquire water as well as food. Foot rot is stimulated while a cut rather scrape on the skin that permits disease to go through between the claws as well around the upper of the hoof.









 Lead poisoning: Sunken abdominal pain and calf is dull are the major symptoms of lead poisoning. It mainly occurs when they lick the metalwork, painted tarpaulins, lead batteries etc.
Lead poisoning: Sunken abdominal pain and calf is dull are the major symptoms of lead poisoning. It mainly occurs when they lick the metalwork, painted tarpaulins, lead batteries etc.



















