General Information
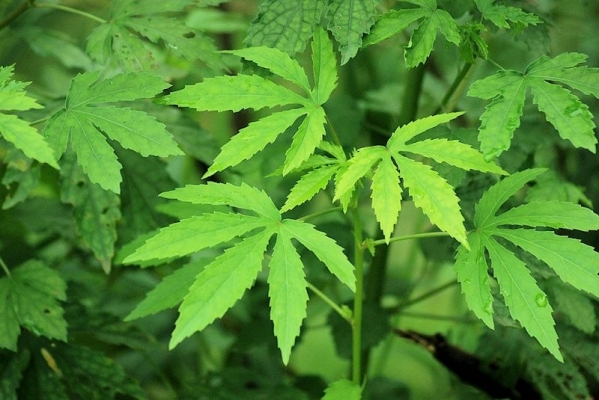
Mesta is herbaceous annual plant. It is an important commercial crop after cotton and Jute. Its origin lies in Afro-Asian countries. Stem or bark of plant is used for fibre production. Hibiscus cannabinus and Hibiscus sabdariffa are two species commonly name as Mesta. Hibiscus Sabdariffa is drought resistant variety where as in areas of rainfall of 50-90 mm canabiscus grow well as it is short duration variety. Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, Bihar, Orissa, Meghalaya, Karnataka and Tripura are major mesta growing states.