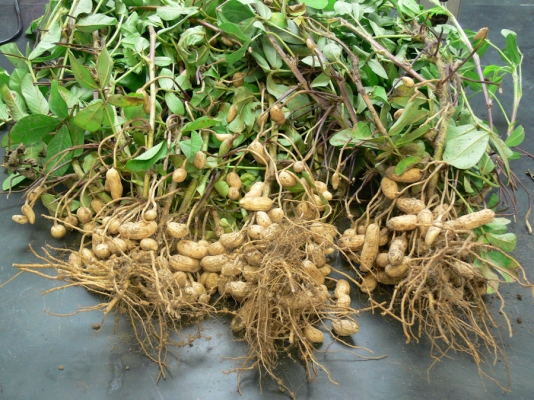
TG37A: The variety is suitable for spring season. The shelling out turn is 65% and the average weight of 100 kernels are 42.5gm. The kernels are spherical in shape and pink in color. It gives an average yield of 12.3qtl/acre of pods.
PG-1: It is a spreading variety recommended for cultivation under rain fed conditions in Punjab. Ready to harvest in 130 days. It has a shelling percentage of 69. It yields about 6-8 quintals per acre. Seeds contain 49 per cent oil.
C-501 (Virginia group): It is a semi-spreading variety recommended for cultivation in sandy loam and loamy soils under irrigated conditions where spreading varieties do not grow well. It yields about 10 quintals per acre. It matures in about 125-130 days. It has 68 per cent shelling out turn and 48 percent oil content.
M548: Grown in sandy areas of the place with certainly dispersed rain fall of about 550 mm in July, mid-august as well as September or simply under deterrent irrigation. Ready to harvest in 123 days. Crude oil content obtained is 52.4%.
M-335: It is a spreading variety recommended for cultivation in Punjab. It matures in 125 days. It has a shelling percentage of 67. It yields about 8-10 quintals per acre. Seeds contain 49 percent oil. It is recommended for sowing under irrigated conditions in Punjab.
M-522: It is a spreading variety for sowing under irrigated conditions in Punjab. It matures in about 115 days. It has a shelling out turn of 68 percent. Seeds contain 50.7 percent oil. Pods are medium bold in size with mostly two kernels. Its yield potential is 9 quintals per acre.
M-37: Crop size is 25cm, a scattering kind variety with trailing divisions, foliage is big in dimensions, densely organized as well as deep greenish in shade. Pods are 1 to 2 seeded hardly ever 3-seeded. Shelling is 69%.
SG 99: This variety is grown in loamy sand to sandy places throughout summer months. Period of maturity is 124 days; principle stalk length is 66-68 cm; mature pods/plant is 22-24 in number; hundred kernel weights is 54; shelling out turn is 66%; oil content produced is 52.3. Average pod yield is about 10qtl/acre. Tolerant to bud necrosis disease.
SG-84: It is a bunch type variety suitable for growing in Punjab. It matures in 120-130 days. Seeds are of light brown color and contain 50 percent oil. It has a shelling out turn of 64 percent. Its yield potential is 10 quintals per acre.
Moongphali No. 13: It is a spreading variety with profuse lateral branches and vigorous growth. It is recommended for cultivation in sandy soils. It matures in 125-135 days. Its yield potential is 10-12 quintals per acre. It has 68 percent, shelling out turn. Seeds are of bold size and contain 49 percent oil.
M-145: A semi growing kind. Ideal for cultivation under irrigated as well as rain fed situations. Foliage is light greenish. Pods 1-4 seeded with purple tinted kernels. Shelling is 77%. Hundred kernels weight about 51gm. Proteins amount contains 29 .4%. It matures within 125 days.
M-197: It is a semi spreading variety recommended for cultivation in Punjab. It matures in 118-120 days. It has a shelling percentage of 68. It yields about 7-9 quintals per acre. Seeds contain 51 percent oil.
ICGS1: High yielding Spanish bunch type variety. Mature in 112 days. Resistant to bud necrosis disease. 70% shelling turn over and 51% oil content.
AL 882: It is a dwarf and early maturing variety. It gives an average yield of 5.4qtl/acre.
Other state varieties:
GG 21: This variety is has bold kernel size and having attractive tan color. It is having higher pod yield. It is having average kernel yield of 490 kg/acre.
GG 8: It give average yield of 690kg/acre which is 7-15%higher than TAG 24 and JL 24.