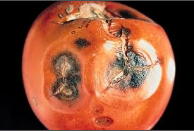
General Information
Tomato is important commercial vegetable crop of India and is second most important crop of world after Potato. Fruits are eaten raw or in cooked form. It is rich source of Vitamin A, C, Potassium and Minerals. It is used in soup, juice and ketch up, powder. The major tomato producing states are Bihar, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, Orissa, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal.
In Maharashtra, near about Fifty Thousand hectare area is under tomato cultivation with production of 1lakh ton. Nashik, Pune, Nagpur, Ahmednagar and Chandrapur are major tomato growing districts, contribute about 75% of total production.