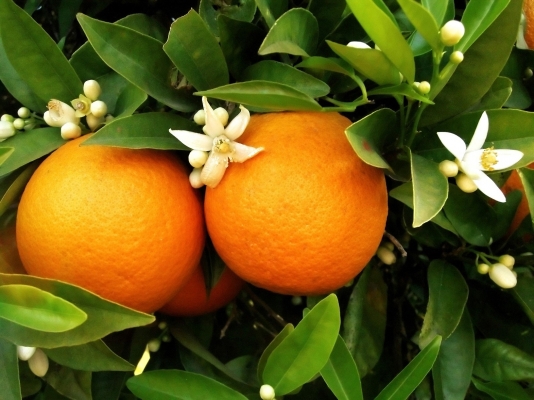
Nurpur Santra: Fruits are medium to large size, long, slightly rounded, deep orange in color, thick peel, and fruit has good fragrance, tasty, juicy, and slightly sour, contains 5-10seeds per fruit, and ripens in mid-December.
Other state varieties:
Kinnow: It is a hybrid variety between King and Willow leaf. Plants are large sized, symmetrical with dense foliage, broad leaves. Fruits are medium in size, deep orange yellow colored on ripening, and Adherent juicy fruit with 12-24 seeds. Fruit matures in the months of January-February. This variety when first introduced into Punjab, performed very well and gained high commercial significance.
Srinagar: Fruits are small to medium size, shining, orange color, long and round in shape, peel is thin and loose, good fragrance, tasty, ripens in end week of December, good yield.
Coorg: Trees are up righted, vigorous having compact foliage. Fruits are bright orange in color, medium to large size, easily peeled with 9-11 segments. It contains abundant Juice with 15-25 seeds. It matures in February-March months.
Khasi: Locally known as Sikkim. It is commercially grown in the states of Assam, Meghalaya. Medium to Large sized trees, dense foliage with thorns. Orange-yellow to bright orange color fruits with smooth surface. Orange color fruits with 9-25 seeds.
Mudkhed, Butwal, Dancy
Kara (Abohar), Darjeeling, Sumithra, Seedless 182