Fertilizer Requirement (kg/acre)
Nutrient Requirement (kg/acre)
| NITROGEN |
PHOSPHORUS |
POTASH |
| 160 |
68 |
68 |
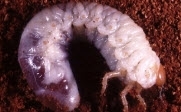
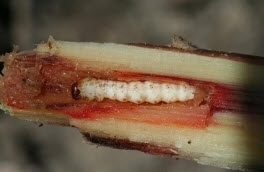
Soil testing after every three year is necessary to know actual need of fertilizer. Before sowing at time of last ploughing, add well decomposed cow dung@8ton or Vermicompost+ Ralligold@8-10kg or PSB@5-10kg per Acre.
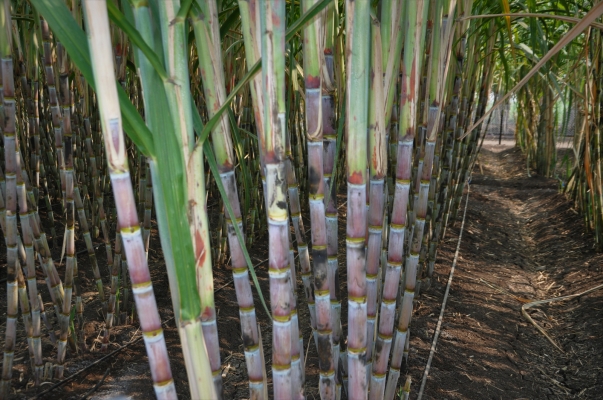
1) In general, for AadSali plantation crop required, Nitrogen@160kg (Urea@350kg), Phosphorus@68kg (SSP@426kg) and Potash@68kg (MoP@115kg/acre).
Apply Urea@35kg, SSP@213 and MoP@57kg at time of sowing.Apply dose of Urea@140kg/acre and 35kg, six to seven week and 12-16th week respectively, after plantation.Apply remaining dose of Urea@140kg, SSP@213Kg and MoP@57kg/acre at time of earthing up operation.
2) For PurvHungami crop, apply Nitrogen@136kg (Urea@296kg), Phosphorus@68kg (SSP@426kg) and Potash@68kg (MOP@114kg) per acre.
Apply Urea@30kg, SSP@213 and MoP@57kg at time of sowing. Apply dose of Urea@118kg/acre and 30kg, six to seven week and 12-16th week respectively, after plantation. Apply remaining dose of Urea@118kg, SSP@213 and MoP@57kg/acre at time of earthing up operation.
3) For Suru crop, apply Nitrogen@100kg (Urea@220kg), Phosphorus@46kg (SSP@288kg and Potash@46kg (MoP@80kg) per acre.
Apply Urea@22kg, SSP@150kg and MoP@40kg at time of sowing. Apply dose of Urea@88kg/acre and 22kg, six to seven week and 12-16th week respectively, after plantation. Apply remaining dose of Urea@88kg, SSP@138kg and MoP@40kg/acre at time of earthing up operation.
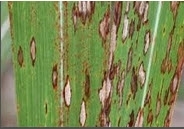
In winter, due to low temperature uptake of nutrient by crop become less and plant give yellow appearance. To recovered crop, take spray of 19:19:19@100gm/15Ltr of water. In water scarcity situation spray of Urea+Potash@2.5kg/100Ltr is helpful for crop.