Climate
-
Temperature
20-30°C -
Rainfall
50-75cm -
Sowing temperature
25-35°C -
Harvesting temperature
18-25°C









Groundnut is a significant oilseed, ideal for cultivation in tropic regions of the country. Groundnut (Arachis hypogaea), is a species in the legume or "bean" family. It is considered to be local in South America. These are known by many other local names such as earthnuts, ground nuts, goober peas, monkey nuts, pygmy nuts and pig nuts. Despite its name and appearance, the peanut is not a nut, but rather a legume.
Groundnut is the third most important oilseed of world. In India, it is available throughout the year. It is important source of protein grown mostly under rain-fed conditions. In India, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujrat, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Tamilnadu are major groundnut growing states. In Haryana, around 5000 ha area is under groundnut cultivation.








Groundnut is raised in a sandy loam as well as well drained sandy clay loam soil. Deep well- drained soil with pH of 6.5 -7 as well as having great fertility are perfect for groundnut cultivation. Heavy and stiff clays are unsuitable for groundnut cultivation as the pod development is hampered in these soils.
Moongphali Haryana-1: Bunch type variety, ready to harvest in 105-110 days. It give average yield of 7-9 qtl/acre.
Moongphali No. 13: It is a spreading variety with profuse lateral branches and vigorous growth. It is recommended for cultivation in sandy soils. It matures in 125-135 days. Its yield potential is 8-13 quintals per acre. It has 68%, shelling out turn. Seeds are of bold size and contain 49 percent oil.
Moongphali Haryana-2: Bunch type variety ready to harvest in 105-110 days. It gives average yield of 7-8 qtl/acre.
M-145: A semi growing kind. Ideal for cultivation under irrigated as well as rainfed situations. Foliage is light greenish. Pods 1-4 seeded with purple tinted kernels. Shelling is 77% . Hundred kernels weight about 51 gm. Proteins amount contains 29 .4%. It matures within 125 days.
PG-1: It is a spreading variety recommended for cultivation under rainfed conditions in Punjab. Ready to harvest in 130 days. It has a shelling percentage of 69. It yields about 5.6-6.4 quintals per acre. Seeds contain 49 per cent oil.
MH-4: Dwarf variety suitable for cultivation under irrigated areas. Ready to harvest in 115 days. Show resistance to tikka disease. It gives average yield of 7-9 qtl/acre.
Other states Varieties
GG 21: This variety is has bold kernal size and having attractive tan color. It is having higher pod yield. It is having average kernal yield of 490 kg/acre.
GG 8: It gives average yield of 690 kg/acre which is 7-15% higher than TAG 24 and JL 24.
After harvesting of previous crop, plough the land twice and pulverised soil to obtain good tilth. If necessary, give third ploughing for rainfed crop. Use harrow or tillers for cultivation purpose. When land is heavily infested with perennial weeds very deep ploughing is needed. For irrigated crop, make beds of convenient size depending upon topography, nature of irrigation source etc.
Avoid sowing groundnut in the same field year after year, as this practice results in heavy build- up of soil-borne diseases.
Time of sowing
Sow the rainfed crop with the advent of monsoon in the last week of June or in the Ist week of July. Complete sowing as early as possible as delay sowing results in reduction in yield.
Where irrigation facility is available, sow kharif groundnut from April end to May end.
Spacing
Spacing to be adopted is depends upon the type of variety i.e for semi spreading variety use spacing of 30cm between the rows and 22.5cm between plants and for bunchy type varieties use spacing of 30x15cm.
Sowing Depth
Pods are sown with help of seed drill or pora at depth of 5cm.
Method of sowing
seeds are sown with help of seed drill or pora method.
ICRISAT method: Technology from China. In this technology, broad beds and furrows are formed along with polyethylene film mulched. It has several advantages like crop matures about 10 days earlier than under non-mulched condition, minimize weed infestation etc.
Make beds of 60cm width and leave 15cm on the either side for the furrows. In a plot size of 4.5m x 6.0m, five beds can be made. After the formation of the bed and fertilizer application, spread black polythene sheet (90cm width) over the soil surface. Polyethylene sheet of seven micron @20kg/acre is required. Holes can be made at required spacing of 30 x10cm before spreading of the sheets. The seed requirement is similar to normal groundnut cultivation.
Seed Rate
For sowing use seed rate of 38-40 kg/acre.
Seed Treatment
Use healthy and well developed kernals for sowing. Carry out seed treatment with Thiram@5gm or Captan@2-3 gm/kg or Mancozeb@4 g/kg or Carboxin or Carbendazim@2 gm/kg of the kernals to avoid infestation from ground borne disease. After chemical treatment, treat the seeds with Trichoderma viride@4 g/kg seed or Pseudomonas fluorescens@10 gm/kg seed. Seed treatment will protect the young seedlings from root-rot and collar rot infection.
| Fungicide name | Quantity (Dosage per kg seed) |
| Carbendazim | 2gm |
| Captan | 2-3gm |
| Thiram | 5gm |
| Mancozeb | 4gm |
| Chloropyriphos 20EC | 12.5ml |
Fertilizer Requirement (kg/acre)
| UREA | SSP | MOP |
| 13 | 125 | 17 |
Nutrient Requirement (kg/acre)
| NITROGEN | PHOSPHORUS | POTASH |
| 6 | 20 | 10 |
Apply fertilizer dose depending upon soil testing. Apply Urea@13 kg/acre, SSP@125 kg/acre and depending upon soil testing if soil show deficiency of potash then apply 10 kg/acre of MoP. Also apply zinc sulphate@10 kg/acre. Drill all fertilizers at time of sowing. Application of gypsum is helpful as it encourages pod formation and better filling up of the pods.
Water Soluble Fertilizer: To improve pod filling spraying of nutrient solution is important. This can be prepared by soaking DAP@2.5 kg, Ammonium sulphate@1kg and Borax@500 gm in 37 lit of water overnight. The next day morning it can be filtered and about 16 litre of mixture can be obtained and it may be diluted with 234 lit of water so as to made up to 200 litre to spray for one acre. Planofix@350ml can also be mixed while spraying. This can be sprayed on 25th and 35th day after sowing.
Weed control during first 45 days of growth period is essential for good yield. Give two hoeings, the first three weeks after sowing and the second three weeks there after. No interculture would be done after the pegs have commmenced going underground. Apply Fluchoralin @300 gm-500 gm/acre or Pendimethalin@1 ltr/acre as pre-emergence area followed by hand weeding once 36-40 days after planting.
Accomplish earthing up during second hand weeding/late hand weeding (in herbicide application). It is an important operation in groundnut. Earthing up is to be done within 40-45 days after sowing as it helps for the penetration of pegs in the soil and also facilitates for increased pod development.
Irrigation for two or three time depending upon seasonal rainfall is necessary for good crop growth. Apply first irrigation at flowering stage. If the Kharif crop is caught in a long spell of draught, especially at the pod formation stage, supplemental irrigation is given, if water is available (In pod development stage, 2 - 3 irrigations are given depending on the soil type). Another irrigation a few days before the harvest may be given for full recovery for pods from soil.

Aphid: Its infestation is high when rainfall is low. These are black bodied tiny insects suck the sap making the plants stunted and yellow. They secrete a sticky fluid (honeydew) on the plant, which is turned black by a fungus.
It can be controlled by spraying of Chlorpyrifos 20%EC@400ml/acre or Imidacloprid 17.8% SL@40-50ml/acre or Methyl demeton 25%EC@400ml/acre as soon as the symptoms are seen.
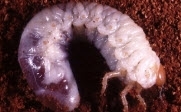
White grub: The adult beetles emerge from the soil during June-July with the first showers of rain. They congregate on the nearby trees such as ber, guava, rukmanjani, grapevines, almonds etc. and feed on their leaves during night. The eggs are laid in the soil and the larvae (grubs) hatching from them eat away the rootlets or root hairs of the groundnut plants.
For effective management of white grub. Plough the field twice during May-June. It exposes the beetles resting in the soil. Do not delay crop sowing. Before sowing treat the seed with Chlorpyriphos 20EC@12.5ml per kg kernels. For beetle control, spray with carbaryl@600gm/100Ltr of water. The spray should be repeated after every rainfall till the middle of july. Apply Phorate@4kg or carbofuran@13kg per acre in the soil at or before sowing.

Hairy caterpillar: The caterpillars occur in masses and defoliate the crop, reducing the yield. Larvae is reddish brown with black band and redish hairs on all over body.
Set up 3-4 light traps immediately after receipts of rains. Collect and destroy egg masses in the cropped area. Avoid migration of larvae by digging a trench 30 cm deep and 25 cm wide with perpendicular sides around the infested fields. Distribute small balls of poison bait in the field during evening hours. To prepare poison bait, mix 10 kg of rice bran, 1kg jaggery and one liter Quinalphos. To control young larvae, do spray of Carbaryl@600-800gm or Quinalphos at 250-300 ml/acre. To control grown up caterpillar, spray with 80ml of Dichlorvos 100EC@200ml/160Ltr water/acre.

Groundnut leaf miner: Young larvae bor into the leaflets and form small purple blotch on the leaf. Later stages larvae web the leaflets together and feed on them, remaining within the folds. Severely attacked field gives "burnt" appearance. Set up light traps @5/acre. Apply Dimethoate 30EC@265 ml/acre or Malathion 50EC@400 ml/acre or Methyl demeton 25%EC@400ml/acre.

Termites: Termites penetrate and hollow out the tap root and stem thus kill the plant. Bore holes into pods and damage the seed. Due to infestation of termite wilting of plant is observed.
Use well decomposed cow dung. Do not delay harvesting of crop. Seed treatment with chlorpyriphos @ 6.5ml /kg of seed may reduce termite damage. Do Dusting of Chlorpyriphos@10-12 kg/acre in soil before sowing in endemic areas.

Pod borer: Holes are observed in young plant that are plugged with excreta. Nymphs are of white in early stages and later turns brown.
Apply Malathion 5D@10 kg/acre or Carbofuran 3%CG@10 kg/acre, on soil at 40 days prior to sowing on infected area.

Tikka or Cercospora Leaf-spot: Necrotic circular spot surrounded by a light-yellow ring on the upper side of the leaves.
To control the disease take care from starting, from selection of seeds. Select healthy kernels. Before sowing do seed treatment with Thiram (75%)@5gm or Indofil M-45 (75%)@3 gm/kg of kernels. Spray the crop with Wettable sulphur 50WP@ 500-750gm/200-300 Litres of water per acre. Give 3 or 4 sprays at fortnightly intervals, starting from the first week of August. Alternatively, spray the irrigated crop with Carbendazim@400-500gm/100Ltr of water per acre. Give three sprays at fortnightly intervals, starting when the crop is 40 days old.

Collar-rot and Seed rot: These diseases are caused by Aspergillus niger. Causes rooting of the hypocotyl region, wilting and death of the seedlings. To control seed treatment is necessary. Treat the seed with Thiram or Captan 3 gm/kg of seed.
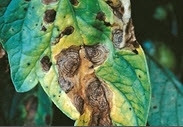
Alternaria leaf disease: Characterized by blighting of apical portions of leaflets which turn light to dark brown colour. In the later stages of infection, blighted leaves curl inward and become brittle.
If infestation is observed, do foliar application of Mancozeb@3 gm/Ltr or Copper oxychloride@3 gm/acre or Carbendazim@4gm/Ltr of water.

Rust: Pustules appear first on the lower surface of leaf. They may be formed on all aerial plant parts apart from flower and pegs. Severely infected leaves turn necrotic and desiccate but are attached to the plant.
After infestation is observed, take spray of Mancozeb@400gm/acre or Chlorothalonil@400gm/acre or Wettable sulphur@ 100 gm/acre. If necessary take second spray with interval of 15 days.
Potassium Deficiency
Leaves are not growing properly and grows in irregular shape. Mature leaves show pale yellow appearance and veins remain green. To overcome deficiency applies Muriate of Potash@16-20 kg/acre.
Calcium Deficiency
Mostly observed in light soils or alkaline soils. Plants not grow properly. Leaves show curling up. To overcome this deficiency applies Gypsum@200 kg/acre at peg formation stage.
Iron Deficiency
Entire leaf gets white or chlorotic. If deficiency is observed, spray crop with ferrous sulphate@5gm + citric acid@1gm/Ltr of water with one week interval. Continue spraying till deficiency gets disappeared.
Zinc Deficiency
Affected plant shows leaves in cluster form, leaves growth get stunted and appear small.
Take spray of Zinc sulphate@2 gm/Ltr of water. Spray for two-three times with 7 days interval.
Sulphur Deficiency
Young plant growth get stunted and appeared smaller in size. Also leaves are small and give yellowish appearance. Maturity of plant gets delayed.
As a preventive measure apply Gypsum@200 kg/acre at planting and pegging stage.
Crop is ready to harvest when plant show uniform yellowing of crop along with shedding of older leaves. For efficient harvesting of crop, adequate moisture should be present in soil and crop should not be over riped. Harvested plants are stacked for a few days for drying. After then, bring crop at one place and give 2-3 shakings and beatings daily for 2 to 3 days with a toothed rake or trangli to separate pods and leaves. Dried pods in sun for 4 or 5 days before storage.
On cloudy days removed pods and then immediately place them in an air drier@27-38 degree centigrade for 2 days or until pods dry to constant mass (6-8%).
After cleaning and grading, store pods in gunny bags and stack them up to 10 bags high in separated stocks so that air freely circulate among them. The bags should be piled on wooden plank to avoid damage due to dampness.
Processed Peanuts: Apart from raw edible peanuts, India is also in a position to supply blanched peanuts, roasted salted peanuts and dry roasted peanuts and a variety of peanut based products.
1.Punjab Agricultural University Ludhiana
2.Department of Agriculture
3.Indian Agricultural Research Instittute, New Delhi
4.Indian Institute of Wheat and Barley Research
5.Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare
You have successfully login.
Your email and password is incorrect!