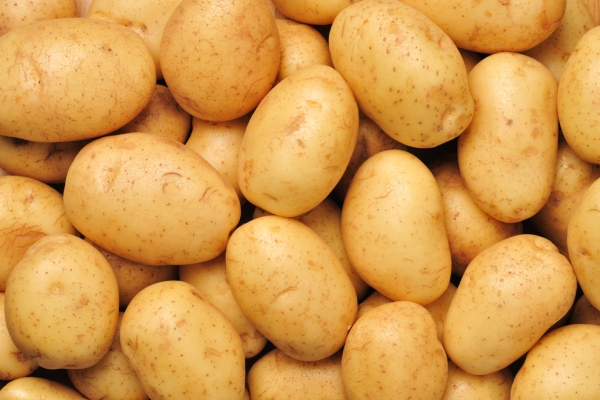
Kufri Chandramukhi: It is an early maturing variety and is suitable for sowing in ground areas to mountainous areas. The variety gets ready in 110-130 days. It has medium height plant, early maturing and flowers are light pink in color. Tubers are of large oval shape which are slightly flattened and having dull white color flesh. In high mountainous areas, it gives an average yield of 37.5-41qtl/acre and in dry temperate areas; it gives an average yield of 100qtl/acre.
Kufri Jyoti: It is a medium season variety which gets ready in 130-150 days. It has long, straight, early growers and medium size variety. It bears white color flowers. The variety is resistant to wilting. It is a high yielding variety. It gives an average yield of 62.5-72qtl/acre.
Other state varieties:
White skin varieties
Kufri Ashoka (PJ 376): It is developed by CPIU, Shimla and suitable for cultivation in Bihar, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal. Plant is of medium height with medium thick stem. It gets mature in 70-80 days. Tubers are of large oval shape, white color with smooth skin. It is susceptible to late blight.
Kufri Bahar: Plants are tall with thick stem, 4-5 stem per plant. Tubers are of large, white, round to oval shape and flesh is of white color. It matures in 90-100 days and gives yield of 100-120qtl/acre. Its keeping quality is average. It is resistant to late blight, early blight and leaf roll etc.
Kufri Pukhraj: Plants are tall with medium thick stems, stems are few. Tubers are of white, large and oval shape with smooth skin. It matures in 70-90 days and gives average yield of 160qtl/acre. It is resistant to early blight and not suitable for processing.
Kufri Badshah: Plants are tall with 4-5 stems per plant. Tubers are of large to medium, oval shape with dull white flesh. Tubers are tasty with good flavor. It matures in 90-100 days. It is tolerant to frost, resistant to late blight, early blight.
Kufri sutlej: Plants are medium compact and thick stem. Foliage is of gray green color. Tubers are large size with oval shape and smooth skin. It matures in 90-100 days with average yield of 160qtl/acre. It has good consumer quality, it easy for cooking with mild flavor. It is not suitable for processing.
Red skin varieties
Kufri Sindhuri: Suitable for Karnataka, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Jammu and Kashmir and Punjab. It has medium round shape tubers having deep red eyes. The variety is moderately resistant to early blight and tolerant to Potato Leaf Roll Virus (PLRV) and late blight disease. It gets mature in 110-120 days and gives an average yield of 165qtl/acre.
Kufri Lalima: Suitable for Bihar and Uttar Pradesh states. It has medium round shape tuber. The variety matures in 100-110 days. It gives an average yield of 165qtl/acre. The variety is moderately resistant to early blight.
Suitable varieties for processing
Kufri Chipsona 1: Suitable for Bihar and Uttar Pradesh. It has medium to large tuber having fleet eyes on it. The crop matures in 90-110 days after sowing. It gives an average yield of 165 qtl/acre. The variety is resistant to late blight and is tolerant to frost. It is suitable for making chips and French fries.
Kufri Chipsona 2: Plants are of medium tall with few stems. Foliage is of dark green and flowers are of white color. Tubers are of white, medium size, round, oval shape with smooth skin. Gives average yield of 140qtl/acre. It is resistant to late blight. It is highly suitable for making chips and french fries.
Kufri Chipsona 3: Medium duration variety ready to harvest in 100-110 days. Gives average yield of 120-140 qtl/acre.
Kufri Anand: Medium duration variety gives resistant to late blight and frost. Gives average yield of 140-160 qtl/acre.
Kufri Pushkar: Medium duration variety gives average yield of 120-140qtl/acre.