Climate
-
Temperature
24-30°C -
Rainfall
60-90cm -
Sowing Temperature
24-28°C -
Harvesting Temperature
30-32°C

















It can be grown on wide variety of soils. Sandy loam to clay loam is considered to be most suitable soil for gram cultivation. Soil having water logging problem are not suitable for cultivation. Saline alkaline soils are not suitable. pH in the range of 5.5 to 7 is ideal for sowing.
Avoid sowing of same crop continuously in field. Follow proper crop rotation. Crop rotation with cereals will help in controlling soil borne disease. Common rotation are Kharif fallow-chick pea, Kharif fallow- gram + wheat/barley/raya, Chari-gram, bajra-gram, rice/maize-gram.
Arpita (RSG-963): Released by RAU, Bikaner in 2005. Gives an average yield of 6 qtl/acre. It takes 125-130 days to reach maturity. The variety is moderately resistant to dry root rot, wilt and B.G.M.
Aadhar (RSG-963): It is moderatly resistant to Wilt, dry root rot, B.G.M and Collar rot, pod borer, & Nematodes. Ready to harvest in 125-130 days. Gives average yield of 6 qtl/acre.
Abha (RSG-973): Released by ARS, Durgapura in 2006. Gives an average yield of 6 qtl/acre. It takes 120-125 days to reach maturity. The variety is moderately resistant to dry root rot and wilt.
Abha (RSG-807): Released by ARS, Durgapura in 2006. Gives an average yield of 7.5 qtl/acre. It takes 120-125 days to reach maturity. The variety is moderately resistant to dry root rot.
Rajas: Released by MPKV IN 2007. Gives an average yield of 7.5 qtl/acre. It takes 136 days to reach maturity. The variety is resistant to fusarium wilt.
GNG 421 (Gauri): Released by ARS, Sri Ganga Nagar in 2007. Gives an average yield of 7.5 qtl/acre. It takes 127-160 days to reach maturity. The variety is resistant to dry root rot, stunt and wilt.
GNG 1488 (Sangam): Released by ARS, Sri Ganganagar in 2007. Gives an average yield of 7.5qtl/acre. It takes 99-157 days to reach maturity. The variety is resistant to dry root rot and stunt.
RSG 991 (Aparna): Released by ARS, Durgapur in 2007. Gives an average yield of 5-6 qtl/acre. It takes 130-135 days to reach maturity. The variety is resistant to dry root rot, wilt and collar rot.
RSG 896 (Arpan): Released by ARS, Durgapur in 2007. Gives an average yield of 5-6 qtl/acre. It takes 130-135 days to reach maturity. The variety is resistant to dry root rot, wilt and pod borer.
RSG 902 (Aruna): Released by ARS, Durgapur in 2007. Gives an average yield of 6-7 qtl/acre. It takes 130-135 days to reach maturity. The variety is resistant to dry root rot, wilt and pod borer.
RSG 974 (Abhilasha): Released by ARS, Durgapur in 2010. It takes 130-135 days to reach maturity. The variety is resistant to dry root rot, B.G.M, wilt and sterility mosaic.
GNG 1958: Cultivated under irrigated areas also suitable for normal sown irrigated condition. It has brown seed colour. Ready to harvest in 145 days. Gives average yield of 8-10 qtl/acre.
Other state varieties:
PBG 7: Recommended for cultivation in whole Punjab. This variety is moderately resistant to Ascochyta blight and resistant to wilt and dry root rot. Grain size is medium and gives average yield of 8 qtl/acre. It gets mature in 159 days.
CSJ 515: Suitable under irrigated condition, seeds are small and are of brown colour weight 17gm/100 seed. It is moderately resistant to dry root rot, and tolerant to ascochyta blight. Gets mature in 135 days and gives average yield of 7 qtl/acre.
BG 1053: It is a Kabuli variety. It is early in flowering and matures in 155 days. Seeds are creamy white and bold in size. Gives Average yield of 8 qtl/acre. Suitable for cultivation for throughout state under irrigated condition.
L 550: Kabuli variety. Semi spreading and early flowering variety. Matures in 160 days. Seeds are of creamy white color. It gives average yield of 6 qtl/acre.
L 551: It is kabuli variety. It is resistant to wilt disease. Ready to harvest in 135-140 days. It gives average yield of 6-8 qtl/acre.
GNG 1969: Cultivated under irrigated areas also suitable for normal sown irrigated condition. It possess creamy beige seed colour. Ready to harvest in 146 days. Gives average yield of 9 qtl/acre.
GLK 28127: Suitable for cultivation under irrigated areas, seeds are of large size with light yellow or creamy colour with irregular owl head. Ready to harvest in 149 days. Gives average yield of 8 qtl/acre.
GPF2: The plants are tall with erect growth habit. It is highly resistive to Ascochyta blight and will complex. It gets matures in about 165 days. Gives average yield of 7.6 qtl/acre.
Aadhar (RSG-963): It is moderately resistant to wilt, dry root rot, B.G.M and collar rot, pod borer, & Nematodes. Ready to harvest in 125-130 days. Gives average yield of 6 qtl/acre.
Anubhav (RSG 888): Suitable for cultivation in rainfed area. It is moderately resistant to wilt and root rot. Ready to harvest in 130-135 days. Gives average yield of 9 qtl/acre.
Pusa Chamatkar: Kabuli variety. It is tolerant to wilt. Ready to harvest in 140-150 days. It gives average yield of 7.5 qtl/acre.
C 235: Ready to harvest in 145-150 days. It is tolerant to stem rot and blight disease. Grains are of medium and yellowish brown color. Gives average yield of 8.4-10 qtl/acre.
G 24: Semi-spreading variety, suitable for rainfed conditions. Ready to harvest in 140-145 days. Gives average yield of 10-12 qtl/acre.
G 130: Medium duration variety. Gives average yield of 8-12 qtl/acre.
Very fine and compact seedbed is not good for chick pea, it required rough seed bed. If it is cultivated as mix crop the land should be plough to fine tilth. If chick pea crop is taken after a kharif fallow carry out one deep ploughing during the monsoon as it will help to conserved rain water. Before sowing plough the land only once. If soil appears to be deficient in moisture run a roller about a week before sowing.
Time of sowing
For rainfed conditions, complete sowing from Oct 10 to Oct 25. Under irrigated condition complete sowing from October 25 to November 10 of desi and kabuli varieties. Sowing on right time is necessary as early sowing leads to excessive vegetative growth, also crop get affected due to wilt while late sowing, crop make poor vegetative growth and inadequate root development.
Spacing
For irrigated areas, use row to row spacing of 30cm.
Sowing Depth
For irrigated areas, use seed depth of 5-7cm and for rainfed areas use seed depth of 7-10cm.
Method of sowing
In north India, it is sown by pora method, drilling machine etc.
Seed Rate:
Use seed rate of desi gram 18-20 kg/acre and for kabuli gram 35-40 kg per acre.
Seed Treatment:
Mix Trichoderma@2 kg/acre + decomposed cow dung@50 kg then cover it with jute bags for 24-72 hrs. Then spray this on moist soil before sowing to control soil borne disease. To prevent seeds from soil borne disease they should be treated with fungicide Carbendazim 12% + Mancozeb 63%WP(Saaf)@2 gm/kg of seed before sowing. In termite affected soil, treat seeds with Chlorpyrifos 20EC@10 ml/kg of seeds before sowing.
Inoculate seed with Mesorhizobium, it will increase productivity of gram and increased yield by 7%. For that first moisten seed with water then apply single packet of Meso-rhizobium on seeds. After inoculation dry seeds in shed.
Use any one fungicides from below:
| Fungicide/ insectcide name | Qunatity (Dosage per kg seed) |
| Carbendazim 12% + Mancozeb 63% WP | 2gm |
| Thiram | 3gm |
To keep check on weeds, take first hand weeding or with wheel hoe 25-30 days after sowing and second if needed after 60 days of sowing. Simultaneously for effective weed control, pre-emergence application of Pendimethalin @ 1 litre/150 litre water on third day after sowing for one acre land. It will help for controlling annual weeds. In case of less infestation, hand weeding or inter culture with the help of hoe is always better than herbicides because inter culture operations improve aeration in the soil.
Fertilizer Requirement (kg/acre):
| Crops | UREA | SSP | MOP |
| Desi | 13 | 50 | As per soil test results |
| Kabuli | 13 | 50 | As per soil test results |
Nutrient Requirement (kg/acre):
| Crops | UREA | SSP | MOP |
| Desi | 6 | 8 | As per soil test results |
| Kabuli | 6 | 16 | As per soil test results |
For Desi varieties for irrigated as well as unirrigated areas, apply Nitrogen in form of Urea@13 kg/acre and Phosphorus in form of Super Phosphate@50 kg/acre at time of sowing. Whereas for Kabuli varieties, apply Urea@13 kg/acre and Super Phosphate@100 kg/acre at the time of sowing. For efficient use of fertilizer apply all the fertilizers are drilled in furrows at a depth of 7-10 centimeters.
Mainly Bengal gram farming is done in rainfed areas. If water is available then first irrigation is done after 40-45 days after sowing after flowering and next irrigation is given after pod development. If only single irrigation is available then do it after 60 days of sowing.

Termite: It feeds on root or near root zone of crop. Affected plant show symptom of drying up. It can be easily uprooted. It can affect at seedling stage and also near maturity.
To protect seeds from termite, treat seeds with Chlorpyriphos 20EC@10ml/kg of seeds. If infestation occurs in standing crop, drench with Imidacloprid@4ml/10litre of water or Chlorpyriphos@5ml/10Ltr of water.
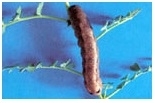
Cut worm: Caterpillar remain hide in soil at depth of 2-4 inch. It cut at base of plant, branches or stem. Eggs are laid down in soil. Larva is dark brown with red head.
Adopt crop rotation. Use only well decomposed cow dung. At early stage pick caterpillar by hand and then destroyed them. Avoid plantation of Tomato. Okra near gram field. In low infestation spray Quinalphos 25EC@400 ml/200-240 liters water per acre. In case of severe infestation Spray with Profenophos 50EC@600 ml/acre in 200-240 liters of water.

Gram pod borer: This is the most serious pest of chickpea and causes damage up to 75% reduction in yield. It feed on leaves causes skeletonization of leaves also feeds on flower and green pods. On pods they make circular holes and feed on grains.
Install Pheromone traps for Helicoverpa armigera@5/acre. In case of low infestation, hand picked grown up larvae. At early stage use HNPV or Neem extract@50 gm/litre of water. Use of chemicals are necessary after ETL level. (ETL: 2 early instar larvae/plant or 5-8 eggs/plant).
Spray Deltamethrin 1%+Triazophos35%@25 ml/10 litre water when crop is at 50% flowering stage. Spray Emamectin Benzoate 5%G@3 gm/10 litre of water 15 days after first spray of Deltamethrin+Triazophos.
In case of severe infestation spray Emamectin Benzoate 5%SG@7-8 gm/15 litre or 20%WG Flubendiamide@8 gm/15 litre water.

Blight: Dark brown spot with dot like bodies developed on stem, branches, leaflet and pods. In case of excessive rain whole plant get severely affected with blight.
For cultivation use resistant varieties. Before sowing carryout seed treatment with fungicide. On incidence of disease spray with Indofil M-45 or Captan @360 gm/100 ltr of water per acre. If necessary repeat the spray at interval of 15 days.

Gray Mold: Small water soaked spots are observed on leaflets. Spots on infected leaves become dark brown. In severe infestation, brown necrotic spots appear on twigs, petioles, leaves and flowers of the plant on attaining full vegetative growth. The affected stem finally breaks and the plant dies.
Before sowing carry out seed treatment. If infestation is observed, spray crop with Carbendazim@2 gm/ltr of water.

Rust: This disease is more severe in Punjab and Uttar Pradesh. Small, round to oval, light or dark brown pustules are formed on the under surface of the leaves. In later stage, pustules get black and affected leaves get defoliate.
Use rust resistant varieties for cultivation. If symptoms are observed spray the crop with Mancozeb 75WP@2 gm/ltr of water. with interval of 10 days take two more sprays.

Wilt: This disease causes considerable loss in yield. In can affect at the seedling stage as well as in an advanced stage of plant growth. Intially affected plant show dropping of petioles and gives dull green color. Afterwards all leaves turn yellow and become straw colored.
Grow resistant varieties. In primary stage of wilt, to control mix 1 kg of Trichoderma in 200 kg well decomposed cow dung and keep it for 3 days, then apply it in wilt affected area. If wilt is observed in fields, spray 300 ml Propiconazol with 200 litre of water per acre.
When plant gets dry and leaves turn reddish brown and start shedding, plant is ready to harvest. Cut the plant with sickle. Sundry the harvested crop for five to six days. After proper drying, carry out threshing by beating the plants with sticks or by trampling under the feet of bullocks.
Grains of harvested crop must be well dried before storage. And take care to avoid the pulse beetle infestation in storage.
You have successfully login.
Your email and password is incorrect!